Key Takeaways
- Cloud security involves comprehensive services that need a wide range of practices and tools designed to protect data, applications, and infrastructure in cloud environments.
- Understanding the shared responsibility model clarifies the roles and responsibilities of cloud providers and businesses in maintaining a secure cloud environment.
- The benefits of robust cloud security services extend to enhanced data protection, reduced security risks, and minimized security incidents and data breaches.
What is Cloud Security?
Cloud security includes a comprehensive range of security policies, procedures, tools, and technologies designed to protect user’s sensitive data, applications, and infrastructure within cloud computing environments.
What are Cloud Security Services?
Cloud Security Services involve a broad range of tools, measures, and practices provided by Cloud Service Providers to safeguard cloud environments. Cloud security services help organizations meet the unique security challenges that arise when they migrate their data and operations to the cloud.
Cloud security services are designed to eliminate security risks and a wide range of threats, such as data breaches, unauthorized access, and other security vulnerabilities, and ensure compliance with established security standards. They address specific aspects of security to strengthen the overall safety of cloud systems.
Cloud Security Services helps to protect your data by ensuring:
- Data Privacy: Cloud security is vital to safeguard personal and sensitive information, ensuring it remains private and secure.
- Data Integrity: It helps maintain the accuracy and reliability of data, preventing unauthorized modification or corruption.
- Compliance: Cloud compliance measures are necessary to meet industry-specific regulatory requirements and legal standards for data handling.
- Business Continuity: Robust cloud security safeguards data against loss or compromise, supporting uninterrupted business operations.
- Cost Savings: Proactive cloud security investments save businesses from the potentially high costs of security breaches and data loss.
Key Pillars (Key Components) of Cloud Security Services
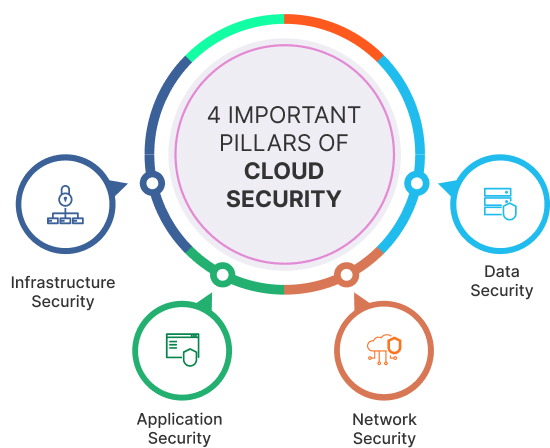
Cloud security involves creating a framework that addresses a wide range of security concerns, ensuring that data, network infrastructure, and applications remain protected and resilient in cloud environments. The 4 important pillars of cloud security services are:
-
Data Security
Data security in the cloud involves protecting the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data stored and transmitted within cloud systems. It involves measures such as encryption to ensure that data remains unreadable to unauthorized individuals, access controls to manage who can access and manipulate data, and data loss prevention (DLP) solutions to prevent unauthorized data leakage.
-
Network Security
Network security primarily focuses on protecting the communication channels and data flows within an organization's network. Common network security measures include Firewalls to filter and control network traffic, Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) for secure remote access, Access controls to manage who can access network resources, and Encryption to protect data in transit.
-
Application Security
Application security is dedicated to safeguarding cloud-based applications from threats and vulnerabilities. It involves secure coding practices, regular assessments, and Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) to identify and mitigate potential security flaws. Application security ensures that cloud applications are resilient to common cyber threats and vulnerabilities, providing a secure user experience.
-
Infrastructure Security
Infrastructure security involves protecting all the underlying physical and digital assets that support an organization's IT environment such as servers, data centers, and physical facilities. Infrastructure security includes physical security measures such as access control systems, surveillance, and secure server rooms, server, and endpoint security to protect individual devices and servers.
What are the Different Types of Cloud Security Services?
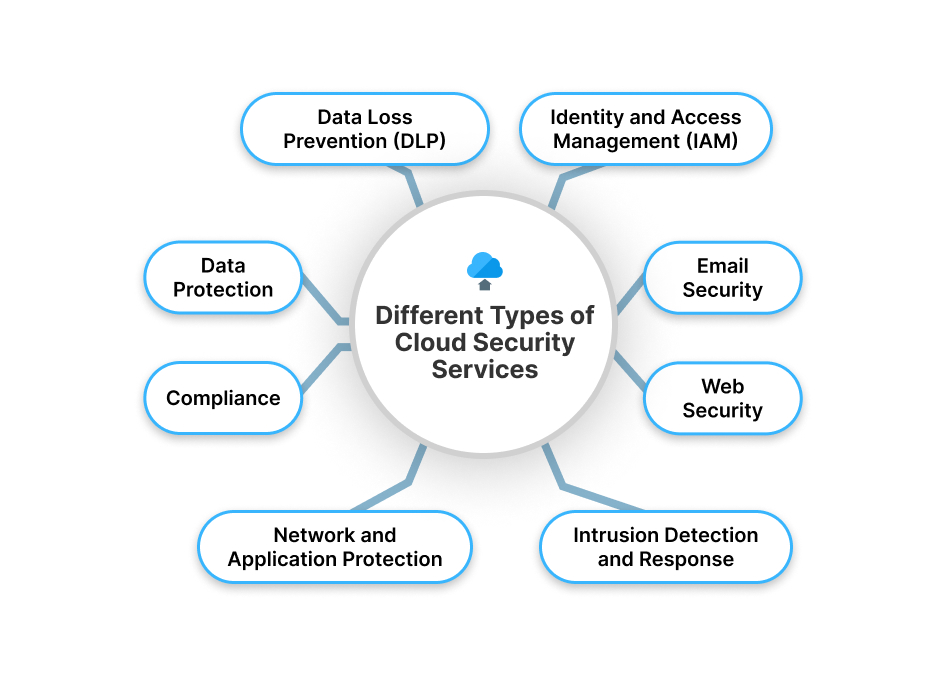
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Data Loss Prevention (DLP) services are dedicated to safeguarding your sensitive data, such as credit card information or personal health records, from accidental exposure or malicious access. By utilizing DLP services organizations can reduce the risk of data breaches and maintain the confidentiality of critical information.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): IAM services ensure that the right individuals within an organization have the correct level of access to cloud resources based on their specific roles or responsibilities. IAM services help organizations handle the complex task of managing user permissions, simplify access control, reduce the risk of unauthorized access, and improve the overall security posture of their cloud systems.
- Email Security: It safeguards against email-related threats including phishing attempts and malware attacks, which often serve as the entry point for cybercriminal activities. These services work persistently to identify and counteract malicious emails, suspicious attachments, and links, preventing cyberattacks from gaining access to your systems through deceptive emails.
- Web Security: Regardless of their location, web security protects your online activities and connections from a wide range of cyber threats. Users access these cloud services from various locations whether in their corporate headquarters, remote offices, or even from home. With web security measures, you can confidently access websites and web-based applications ensuring that your online interactions are fortified against potential threats.
- Intrusion Detection and Response: Intrusion-detection solutions typically scrutinize both inbound and outbound network traffic, identifying any unusual or suspicious activities and promptly detecting potential threats. This is often achieved through advanced pattern recognition mechanisms that analyze specific signatures and behaviors associated with known threats.
- Network and Application Protection: These services enforce security policies and inspect network traffic to prevent unauthorized access at various points, providing multi-layered protection for your network. They allow you to scrutinize and filter traffic, reducing the risk of unauthorized access at various levels, including host, network, and application boundaries.
- Data Protection: Data protection services help to safeguard your data and workloads from unauthorized access through key management, and data discovery services. It ensures the confidentiality and integrity of your information stored in the cloud.
- Compliance: Cloud security services help organizations maintain compliance by providing an overview of their compliance status and conducting automated compliance checks based on industry standards. This ensures that your cloud environment aligns with regulatory requirements and industry-specific best practices, minimizing compliance-related risks.
Why is the Cloud Security Services Important for Organizations?
Migrating to the cloud from traditional legacy systems can significantly enhance your organization's security posture. Cloud computing services, whether in the form of private cloud or public clouds, offer inherent advantages that go beyond the capabilities of traditional, on-premises solutions.
There are several reasons why businesses opt for cloud security services to strengthen their security:
-
Access to Professional Security Expertise
Cloud security service providers (CSPs) specialize in security, surpassing the capabilities of many organizations managing legacy systems. They have dedicated teams focused on security, reducing the risk of human error.
-
Constant Updates and Patching
Cloud service providers regularly update and patch their systems to protect against emerging threats. In legacy systems, organizations may struggle to keep up with these updates, leaving vulnerabilities unaddressed.
-
Reliable Redundancy and Failover
Cloud providers offer redundancy and failover capabilities, ensuring data and applications remain accessible despite hardware failures or natural disasters. This level of resilience can be costly for organizations to implement in legacy systems.
-
Simplified Compliance Management
Many CSPs adhere to strict industry and regulatory compliance standards, simplifying compliance requirements for their customers. In contrast, achieving and maintaining compliance in legacy systems can be complex and costly.
-
Guidance in Security Innovations
CSPs invest heavily in developing and implementing the latest security tools, technologies, and best practices. They often lead in adopting emerging security innovations, providing their clients with advanced protection.
What are the Benefits of Cloud Security Services?
Cloud security is an essential component of modern cybersecurity, providing a wide range of benefits. By implementing cloud security solutions, organizations can achieve numerous advantages that enhance their security, efficiency, resilience, and customer trust.
Here are some key benefits of using cloud security services:
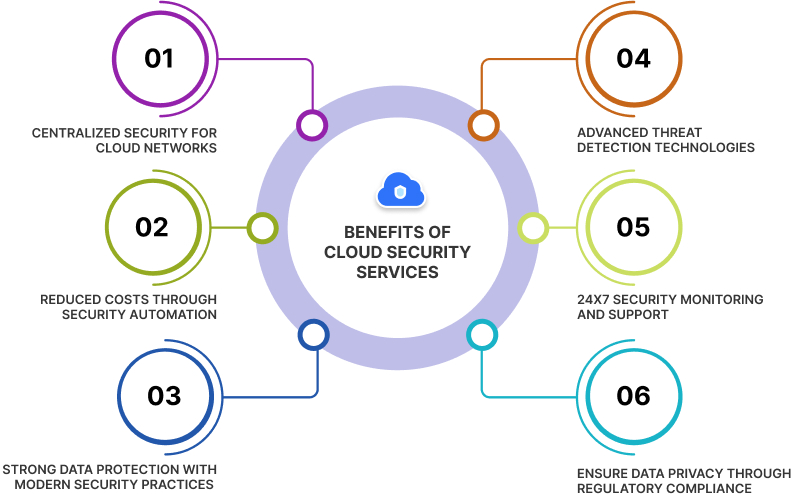
-
Centralized Security for Cloud Networks
With cloud security, you can consolidate protection for your cloud-based networks, enabling simplified monitoring and analysis of various devices and endpoints. It also allows you to manage software updates and policies from a single location and implement disaster recovery plans efficiently.
-
Reduced Costs through Security Automation
Cloud security eliminates the need for expensive dedicated hardware and valuable resources for handling security updates and configurations. Cloud Service Providers (CSPs) offer advanced security features that provide automated protection, often requiring minimal human intervention.
-
Strong Data Protection with Modern Security Practices
Leading cloud computing providers prioritize data security by design, offering robust access controls, data encryption for data at rest and in transit, and data loss prevention (DLP) measures to secure your cloud data, regardless of its location or management.
-
Advanced Threat Detection Technologies
Reputable CSPs invest in cutting-edge technologies and highly skilled experts to provide real-time global threat intelligence. This helps in the detection of both known and unknown threats, both in the wild and within your networks, leading to faster remediation.
-
24x7 Security Monitoring and Support
Most cloud service providers offer round-the-clock monitoring of applications and cloud-based assets, ensuring continuous visibility into your organization's risk posture and its impact on the business.
-
Ensure Data Privacy Through Regulatory Compliance
Cloud providers follow international and industry regulations and undergo strict independent evaluations of their security, privacy, and compliance practices. This simplifies compliance for their customers and guarantees the security of data stored in the cloud.
What are the Common Cloud Security Risks and Challenges?
Even though the cloud is considered secure for storing sensitive data, cloud-based systems present their unique set of risks, threats, and challenges. Within a cloud environment, there are various potential threats and risks that can impact the system's security and data confidentiality, including:
- Data Breaches: A data breach is a security incident where unauthorized individuals gain access to sensitive data stored in cloud systems. Skilled hackers typically target confidential information, including medical records, financial data, and customer information, posing privacy and financial risks to individuals and businesses.
- Data Loss: Data loss in cloud systems refers to the accidental or intentional deletion or corruption of data. Data loss can occur due to various factors, including data breaches, natural disasters, or system-wide malfunctions. Data loss can also occur during data migration to a new environment or when creating backups of the current one.
- Account Hijacking: Account hijacking in cloud security is a significant threat, where cyber attackers gain unauthorized control of cloud-based accounts. Once in control, hackers can access and steal your credentials and sensitive information, including highly confidential customer or corporate data for businesses.
- Malware and Ransomware: Malware and ransomware are dangerous software that can pass into cloud systems without user consent. They can potentially gain access to the cloud by corrupting its security measures. Once inside, it operates in sync with the cloud service, enabling it to steal, manipulate, or withhold data. This puts your information at risk and may lead to data breaches or blackmail attempts.
- Insider Threats: Insider threats in cloud security involve the misuse of cloud resources intentionally or unintentionally by individuals or employees who already have access to your sensitive data, intellectual property, and knowledge of business processes and policies. They may neglect established cloud security protocols, potentially accessing websites or sharing files against company policies, putting privacy and data at risk.
- Misconfigured Cloud Systems: Misconfigurations encompass glitches, gaps, or errors that pose cybersecurity risks during cloud adoption especially when adopting multi-cloud environments to utilize the advantages of various Cloud Service Providers (CSPs). The more cloud networks a business operates concurrently, the harder it becomes to identify and rectify misconfigurations.
- Compliance and Legal Issues: Compliance and Legal Issues in cloud security include the risk of not following the essential regulatory requirements and compliance standards while managing data in cloud environments. Non-compliance with these requirements can have serious consequences, including legal difficulties, fines, and damage to an organization's reputation.
In order to handle all the challenges and risks associated with cloud security, various cloud security solutions have been defined. Let's checkout them below:
What are the Different Types of Cloud Security Solutions?
Cloud security is always changing to keep up with new threats. Below are some different cloud security solutions available to help businesses protect their cloud environments, data, and applications against a wide range of threats, ensuring the safety and reliability of modern cloud systems.
How to Enhance the Security of Your Cloud Infrastructure?
Cloud Security Best Practices You Should Know:
By following the cloud security best practices and adopting the right tools, you can strengthen your cloud infrastructure. Here are some of the best cloud security practices you should follow to enhance the security of your data, application, and infrastructure.
-
Implement Strong Data Encryption:
Data encryption involves applying powerful encryption algorithms to safeguard data both while it's stored and while it's being transmitted. This security measure ensures that even if unauthorized access occurs, the data remains incomprehensible without the encryption key.
-
Prepare for Data Backup and Disaster Recovery:
Implement data backup and recovery strategies to maintain business operations in the face of data loss or system failures. These strategies ensure that critical data can be restored, minimizing downtime and disruption.
-
Develop Incident Response and Recovery Plans:
Incident response and recovery plans provide a structured approach to dealing with security incidents, minimizing their impact and speeding up recovery. They are crucial for addressing breaches or disasters effectively.
-
Strengthen User Account Security with MFA:
MFA adds an extra layer of security to user accounts by requiring multiple forms of verification. This can include something the user knows (a password) and something they possess (like a fingerprint scan), reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
-
Protect Containerized Applications:
Container security solutions help protect applications running in containers within cloud environments. This safeguards not only the applications themselves but also their surrounding infrastructure.
-
Identify and Mitigate Security Vulnerabilities:
Use vulnerability scanning and management tools to identify and address security vulnerabilities in your cloud systems and applications. Regular vulnerability scanning helps discover and mitigate potential security weaknesses in your cloud environment, reducing the risk of exploitation by malicious actors.
-
Keep Your Team Informed with Regular Security Training:
Ongoing security training ensures that your IT and security teams remain well-informed about the latest threats and security best practices. It also extends to employees to boost their awareness of security matters.
-
Maintain Compliance and Governance:
Compliance and governance practices are vital for meeting regulatory requirements and adhering to internal policies. This ensures that your cloud operations comply with data protection and privacy regulations, reducing legal risks.
-
Continuously Monitoring and Logging for Suspicious Activities:
Maintain continuous monitoring of your cloud environments to detect any suspicious activities and gather logs for auditing and incident response. This data is essential for auditing and responding to incidents.
-
Implement Firewalls and Network Security Measures:
Implement firewalls and network security solutions to monitor and control incoming and outgoing traffic between your cloud resources and the internet, to maintain a secure network.
-
Conduct Regular Vulnerability Assessments:
Consistent vulnerability assessments help identify and mitigate security vulnerabilities in your cloud systems and applications. You can also apply patch management in a timely manner to reduce the risk of exploitation.
What is Cloud Security Compliance?
Cloud security compliance is the practice of following official standards and rules that govern how data is stored and used, and it's something every business with data in the cloud must consider. These standards can be set by local, state, or national governments, and are often recognized on a global scale. Cloud security compliance services ensure that your data is protected and used responsibly in the cloud.
Why is Cloud Security Compliance Important?
Cloud security compliance is a fundamental part of responsible and secure cloud data management. It ensures that your data remains safe, and your organization operates within the bounds of the law. Compliance activities encompass a wide range of responsibilities, including safeguarding healthcare information, securing cardholder data, and respecting user privacy, helping to prevent data breaches and legal consequences.
Who is Responsible for Cloud Compliance?
Similar to security, cloud compliance is a shared responsibility. Although some organizations have specialized compliance teams to manage compliance tasks, compliance isn't the exclusive responsibility of any one department. It requires collaboration among technical, legal, and leadership teams. Executives and board members connect business objectives with the practical aspects of compliance.
Regulatory Compliance Examples:
There are numerous regulations, standards, and legislation your organizations may need to comply with, including:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): Safeguards individual data privacy and data collection practices in the European Union.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): Ensures data security and patient privacy in healthcare.
- Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002: Focuses on protecting shareholders and the public from financial misconduct.
- Can-Spam Act of 2003: Regulates commercial email practices.
- Dodd-Frank Act:Enhances transparency and accountability in the financial sector.
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS): Protects credit card transactions.
- Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA): Requires annual reviews of information security for federal agencies.
Things To Consider When Choosing Cloud Security Services
When selecting a cloud security service, there are several critical factors to consider to ensure you make the right choice for your organization.
-
Assess Your Security and Compliance Needs
Begin by assessing your specific security requirements. Identify the types of data you handle, the potential threats you face, and your compliance obligations. This understanding will guide you in choosing services that directly address your needs.
-
Check Compliance Service Compatibility
Ensure that the security services you choose aligns with industry-specific compliance standards that are relevant to your business. This is crucial for avoiding legal and financial consequences.
-
Evaluate Provider Reputation:
Research the reputation and track record of the cloud security service provider. Look for reviews, case studies, and customer testimonials to gain insights into their performance and reliability.
-
Consider the Service Scalability:
Ensure that the services can scale with your organization. As your business grows, your security needs will evolve, and the services should be able to adapt accordingly.
-
Assess Security Integration Feasibility:
Evaluate whether the security services can smoothly integrate with your current IT infrastructure and applications. This ensures a smooth transition and minimal disruption to your operations.
-
Support and Training Availability:
Consider the level of support and training provided by the service provider. Adequate training and support are crucial for effectively implementing and maintaining security measures.
-
Performance and Service Reliability
Assess the performance and reliability of the services. Downtime or performance issues can leave your organization vulnerable to security threats.
-
Responsiveness to Security Incidents
Understand how the service provider handles security incidents and breaches. Quick and effective responses are essential to minimize damage in the event of an attack.
-
Examine Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
Review the SLAs provided by the service provider. SLAs outline the level of service you can expect, including uptime guarantees and support response times.
Gsoft Cloud Security Services: How Do We Help Businesses?
Gsoft Cloud, delivers top-tier managed cloud security and compliance services. Our primary goal is to ensure that your cloud environment remains secure, fully compliant, and optimized to its fullest potential. We understand the challenges of securing your cloud environment while meeting industry standards. This is why we offer a wide array of services to safeguard your data and operations.
Cloud security is essential for businesses, regardless of their size. At Gsoft, we understand this well. Our cloud security services are here to safeguard your data, applications, and infrastructure from threats, allowing you to concentrate on business growth. We provide a comprehensive suite of services that ensure your data's security, protect against threats, and ensure compliance with regulations. Contact us today for a free consultation to learn more about our cloud security services and how we can help you protect your business.
FAQs of Cloud Security Services
Q:
How does data encryption work in cloud security?
Data encryption in cloud security involves using cryptographic techniques to transform plaintext data into ciphertext. This ensures that even if unauthorized users gain access to the data, they cannot read it without the correct decryption key. Advanced encryption algorithms like AES are commonly used to secure data during storage and transmission in cloud environments.
Q:
What's the typical recovery time objective (RTO) for disaster recovery in cloud services?
The Recovery Time Objective (RTO) in cloud disaster recovery outlines the maximum acceptable downtime during a disaster. The actual RTO can vary based on your specific disaster recovery strategy, but in cloud services, it's often designed for minimal downtime. The exact duration depends on your disaster recovery plan, which can be customized for your business needs.
Q:
What does the incident response process in cloud security involve?
Incident response in cloud security involves a well-defined process for detecting, analyzing, and mitigating security incidents. It typically includes identifying the incident, containing it to prevent further damage, eradicating the root cause, recovering affected systems, and documenting the incident for future prevention.
Q:
What technologies and strategies are commonly used to prevent unauthorized access to cloud resources?
Preventing unauthorized access to cloud resources is achieved through various methods including:
-
Identity and Access Management (IAM):
IAM systems enforce role-based access, ensuring users only have permissions relevant to their roles.
-
Multifactor Authentication (MFA):
MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification to access resources.
-
Network Security Controls:
Implementing network security controls helps protect cloud resources by monitoring and filtering traffic to prevent unauthorized access.
-
Encryption:
Data encryption secures information during storage and transmission, making it unreadable to unauthorized users.
-
Security Best Practices:
Adhering to industry-standard security practices, such as regular updates and patches, helps prevent unauthorized access to resources.
Q:
How does proactive threat monitoring work to identify potential security risks in cloud environments?
Proactive threat monitoring employs a combination of technologies to identify potential security risks in cloud environments.
-
Proactive Threat Monitoring Tools:
Proactive threat monitoring utilizes a range of tools, including Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solutions.
-
Threat Intelligence Feeds
Real-time threat intelligence feeds are integrated to stay updated on the latest threats and vulnerabilities.
-
Continuous Analysis:
These tools continuously analyze network and system behavior to detect any suspicious activities or potential threats.
-
Real-Time Monitoring::
Proactive threat monitoring operates in real-time, ensuring quick detection and response to security risks.
Q:
Will the implementation of cloud security services impact the performance of cloud-based applications?
The impact on application performance due to cloud security services can vary depending on factors such as the specific security measures implemented, the efficiency of the cloud service provider, and the design of your applications. In many cases, cloud security solutions are optimized to minimize performance impact.
Q:
What Service Level Agreements (SLAs) are available for cloud security services?
The SLAs for cloud security services outline the provider's commitments regarding service availability, performance, response times, and other key metrics. SLAs can vary between providers, and it's important to review them to ensure they align with your business requirements.
Q:
What are some emerging cloud security threats?
Some of the emerging cloud security threats that demand your attention and proactive measures to mitigate are as follows:
- Data Breaches: Unauthorized attempts to gain access to cloud systems and steal sensitive data.
- Misconfigured Cloud Settings: Errors in cloud configurations that can lead to security vulnerabilities.
- Insider Threats: Malicious or negligent actions by authorized users that can compromise data security.
- Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): Persistent, targeted attacks seek to breach cloud environments over an extended period.
- Zero-Day Vulnerabilities: Attacks targeting unknown software vulnerabilities can lead to security breaches.
- Cloud-Native Threats: Threats specific to cloud environments, such as serverless or container-based attacks.
- AI and Machine Learning Exploits: These involve attacks that utilize AI to create more sophisticated and adaptive threats.
- Cryptojacking: Unlawful use of cloud resources for cryptocurrency mining.



